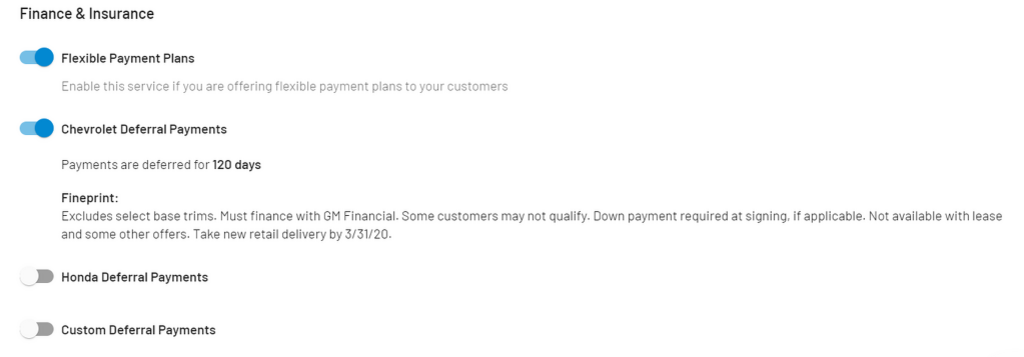
SG&A Expense Selling, General & Administrative Guide, Examples
What’s different is the degree of granularity when reporting operating expenses. General expenses are incurred by a company regardless of the industry or products/services it creates. While reducing SG&A costs can provide a quick boost to profits, it’s important to avoid making cuts that could have a negative impact on long-term profitability. For example, reducing marketing and advertising costs might provide a short-term profit boost, but it could also harm sales in the long term. Once SG&A is deducted from gross profit – assuming there are no other operating expenses – operating income (EBIT) remains.
What is general and administrative G&A expenses?
General and administrative expenses are accounting terms that refer to a company's operating expenses that stay the same regardless of sales or production levels. Types of G&A expenses include building expenses, salaries and wages, insurance, licenses and fees and supplies.
The difference between the SG&A expense and cost of goods sold (COGS) line item is as follows. If SG&A is a consolidated, one-line item, the What Is Selling, General & Administrative Expense Sg&a? analyst must use discretion to select one of these (or other) methods to account for all the various expenses baked into that one line item.
SG&A
A company incurs these expenses regardless of whether they generate or do not generate sales and are typically a significant component of a company’s operating expenses. Indirect selling expenses are incurred during the manufacturing process and after the product is finished. Marketing, advertising and promotion expenses, including social media costs are a good example of indirect selling expenses. Base salaries of salespeople and travel expenses refer to this category as well, even if they don’t generate income. General and Administrative (G&A) expenses are the day-to-day costs a business must pay to operate, whether or not it manufactures products or generates revenue. Typical G&A expenses include rent, utilities, insurance payments, and wages and salaries for administrative and management staff other than salespeople.
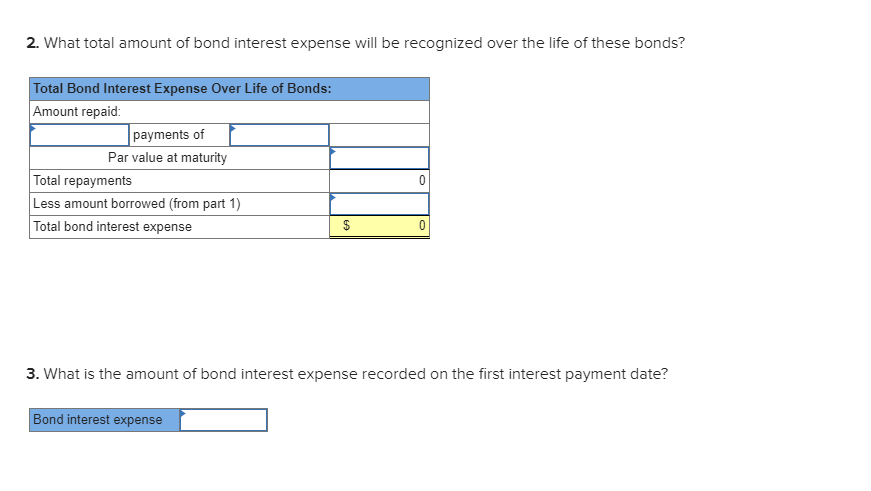
For instance, research and development (R&D) costs are considered SG&A expenses in most industries. Still, in certain industries, such as pharmaceuticals, these costs might be treated as product costs due to their direct relationship with developing new products. At the same https://accounting-services.net/what-is-a-bill/ time the process of gathering business information and turning it into visually perceptible sources for such analysis is streamlined by a good business accounting software. A good combination of Business Intelligence technology and management talent can work wonders.
What’s the difference between SG&A vs. operating expenses?
It’s also important to distinguish your capital expenditure (CapEx) which is what you invest in acquiring, maintaining and upgrading your buildings, machinery and vehicles. The distinction found in the financials will be based on the relative size of each, which depends on the specific industry in question. For example, the SG&A ratio for manufacturers can range anywhere around 20% of revenue, while in healthcare it can be up to 50% of revenue.
In summary, the best way to determine whether an expense is an SG&A cost or a product cost is to examine its relationship to the production process and the company’s overall operations. This evaluation will help ensure that the expenses are classified accurately and in line with accounting principles and financial reporting standards. SG&A expenses can vary significantly from company to company, depending on the business’s size, industry, and nature. It can make it challenging to compare SG&A expenses between companies, and it’s important to consider other factors, such as revenue and operating income when comparing. SG&A expenses provide valuable information for decision-making, as they reflect a company’s operating expenses and efficiency. By tracking SG&A expenses, a company can make informed decisions about investments, cost-saving measures, and other financial initiatives.
Selling, general and administrative expense definition
To calculate a company’s operating income, you subtract operating expenses from its gross revenue. Overall, tracking and managing SG&A expenses is a critical aspect of financial management and can provide valuable benefits for companies and their stakeholders. Remember that the classification of certain costs might depend on the specific context and industry.
SG&A is reported in the section of expenses on a company’s income statement. It has to be noted that SG&A expenses are reported in a company’s income statement under the expenses section. According to Investopedia, SG&A expenses are made of all the costs of running a business that aren’t related to production of goods and services. The SG&A expense is recorded on the income statement of companies in the section below the gross profit line item.
SG&A, or “selling, general and administrative” describes the expenses incurred by a company not directly tied to generating revenue. Some firms classify both depreciation expense and interest expense under SG&A. If this is the case, then gross profit less SG&A equals pre-tax profit, also known as earnings before taxes (EBT).
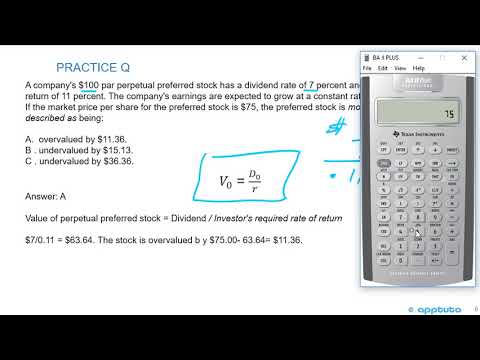
High SG&A costs in relation to revenue can be a problem for almost any business. Management often attempts to keep SG&A costs limited to a certain percentage of revenue, but that figure may vary a great deal, depending on sector and industry. Since commissions are variable costs it’s particularly important to keep an eye on the maximum amounts that are flowing out of your bank accounts here. The same is true of travel costs, such as salespeople visiting clients or attending trade shows as well as staff visiting suppliers or going on buying trips.
How to Calculate SG&A
Companies may aggregate all of these expenses in a single SG&A line, or it may segregate selling costs from general and administrative costs. Firms with highly variable cost structures are said to have low operating leverage. They might have more competition, but they can more easily survive painful declines in revenue and cash flow.
- Larger companies often separate these types of costs into smaller, specific SG&A categories as this is often easier for companies to track and monitor costs in these groups.
- Other SG&A costs, such as shipping costs or sales commissions, will vary.
- The total amount of SG&A for a given period is the sum of all the individual expenses that comprise that category.
- As part of its Q financial reporting, Apple reported $12.809 billion of operating expenses for the quarter.
The sales kept the figures up so the company could avoid cutting spending. Suppose that a bank invests heavily in its customer service experiences. It therefore has higher selling costs on its income sheet, but it also has higher sales. The profitability therefore increases as well, ofsetting those higher costs. Please note that these percentages are rough estimates and can vary from company to company within each industry.
Administrative Expense
This line item includes nearly all business costs not directly attributable to making a product or performing a service. SG&A includes the costs of managing the company and the expenses of delivering its products or services. Administrative expenses are essential for companies and investors, as they can impact a company’s profitability and efficiency. Companies with high administrative fees may not operate as efficiently as those with low overhead costs, which can negatively impact their bottom line.